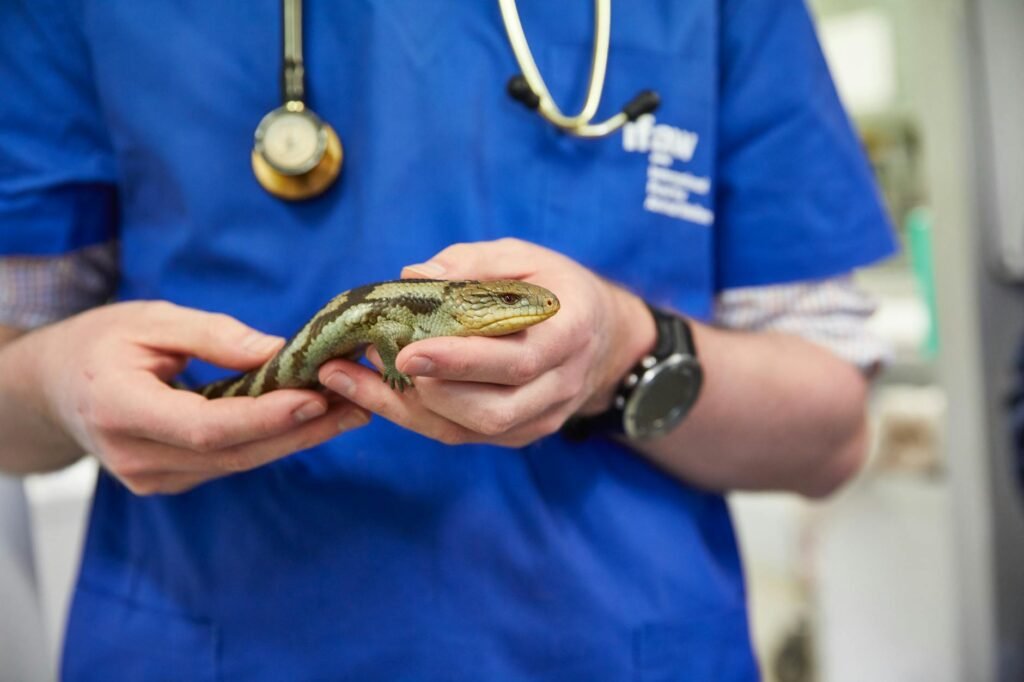
Becoming a veterinary doctor in India is a rewarding and challenging journey that requires dedication, passion, and a well-defined educational path. This guide provides an overview of the steps involved in pursuing a career in veterinary medicine, with a focus on the Indian context.
Educational Path
The path to becoming a veterinary doctor in India typically involves the following stages:
- Higher Secondary Education: Students must complete their 10+2 education with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology as core subjects.
- Bachelor of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry (B.V.Sc. & A.H.): This is a five-year undergraduate program offered by veterinary colleges across India. The course includes classroom lectures, practical training, and internships.
- Veterinary Council of India (VCI) Registration: After completing the B.V.Sc. & A.H. program, graduates must register with the VCI to practice as a veterinarian in India.
Accredited Veterinary Colleges in India
There are several renowned veterinary colleges in India that offer the B.V.Sc. & A.H. program:
- Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Izatnagar, Uttar Pradesh
- Madras Veterinary College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- Bombay Veterinary College, Mumbai, Maharashtra
- West Bengal University of Animal and Fishery Sciences, Kolkata, West Bengal
These institutions are recognized by the VCI and provide a comprehensive education in veterinary science.
Veterinary Curriculum
The B.V.Sc. & A.H. curriculum is designed to provide students with a strong foundation in veterinary science and practical skills. The course is divided into four and a half years of classroom learning and a six-month compulsory internship.
The curriculum covers subjects such as:
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Animal Nutrition
- Veterinary Surgery
- Veterinary Medicine
- Animal Reproduction
- Livestock Production and Management
During the internship, students gain hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating animals under the supervision of experienced veterinarians.
Entrance Exams and Eligibility Criteria
To gain admission into a veterinary college in India, students must meet certain eligibility criteria and clear entrance exams:
- Eligibility: Candidates must have completed their 10+2 education with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology as core subjects. A minimum aggregate of 50% marks in these subjects is required.
- National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET): All medical courses, including veterinary science, require applicants to appear for the NEET exam. The exam is conducted after the 12th grade or after completing a veterinary diploma program.
Specializations and Advanced Studies
After completing the B.V.Sc. & A.H. program, veterinarians can pursue specializations and advanced studies to further their expertise:
- Master of Veterinary Science (M.V.Sc.): This two-year postgraduate program allows veterinarians to specialize in various disciplines such as animal genetics, animal production, veterinary surgery, and more.
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.): Veterinarians can pursue a Ph.D. to engage in advanced research and contribute to the field of veterinary science.
- Diplomate of National Board (DNB): The DNB program is equivalent to an M.V.Sc. and is offered by the National Board of Examinations. It provides specialized training in various veterinary disciplines.
Career Opportunities
Veterinary doctors in India have a wide range of career opportunities:
- Private Practice: Many veterinarians choose to set up their own clinics or join existing practices to provide healthcare services to pets and livestock.
- Government Services: Veterinarians can work in various government departments, such as the Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairy Development, and Fisheries, to contribute to animal health and welfare policies.
- Research and Academia: Veterinarians can pursue research careers in institutions like the IVRI or teach in veterinary colleges.
- Public Health: Veterinarians play a crucial role in public health by monitoring zoonotic diseases, ensuring food safety, and contributing to the One Health approach.
- Animal Welfare Organizations: Many NGOs and animal welfare organizations employ veterinarians to provide healthcare services to stray animals and promote animal welfare.
- Livestock and Poultry Industry: With the growing demand for animal products, veterinarians are needed in the livestock and poultry industry to ensure animal health and productivity.
- Wildlife Conservation: Veterinarians can work in wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, and conservation projects to protect and care for wild animals[3].
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the veterinary profession in India offers numerous opportunities, it also comes with its own set of challenges:
- Infrastructure and Resources: Many veterinary colleges and clinics in India lack adequate infrastructure and resources, which can hinder the quality of education and healthcare services provided.
- Awareness and Pet Ownership: Although pet ownership is increasing in urban areas, there is still a lack of awareness about animal health and welfare in many parts of the country.
- Rural Veterinary Services: Providing veterinary services in rural areas can be challenging due to the lack of infrastructure, transportation, and awareness among farmers.
Despite these challenges, the future prospects for veterinary medicine in India are promising:
- Growing Pet Industry: With the increasing number of pet owners in urban areas, the demand for veterinary services is expected to rise.
- Livestock and Poultry Sector: The livestock and poultry sector in India is growing rapidly, creating a need for more veterinarians to ensure animal health and productivity.
- One Health Approach: The One Health approach, which recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, is gaining traction globally. Veterinarians will play a crucial role in implementing this approach in India.
- Research and Development: As the field of veterinary science advances, there will be more opportunities for research and development in areas such as animal genetics, nutrition, and disease control.
Conclusion
Pursuing a career in veterinary medicine in India is a noble and fulfilling choice. By understanding the educational path, accredited colleges, curriculum, and career opportunities, aspiring veterinarians can make informed decisions and contribute to the health and well-being of animals across the country. Despite the challenges, the future of veterinary medicine in India looks bright, with growing opportunities in various sectors and the potential to make a significant impact on animal and human health.